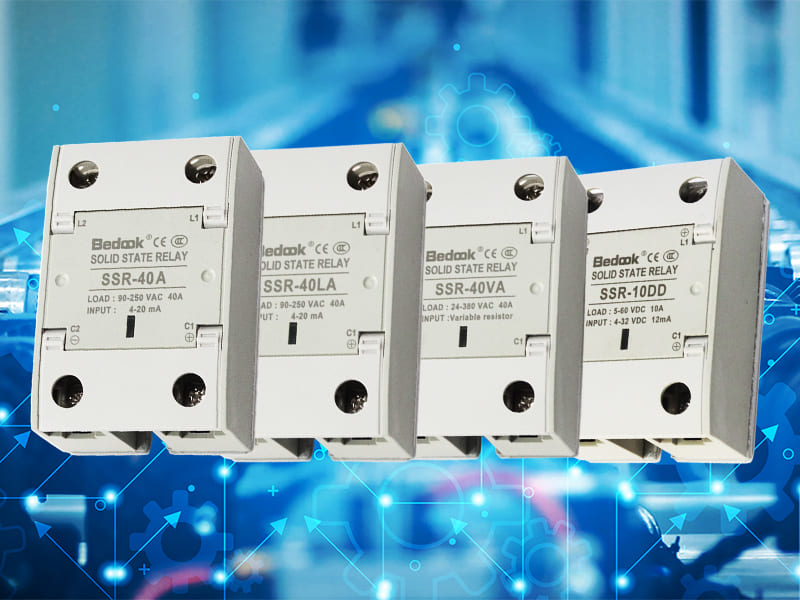
Solid State Relay SSR Classification: A Must – Know for Electrical Projects
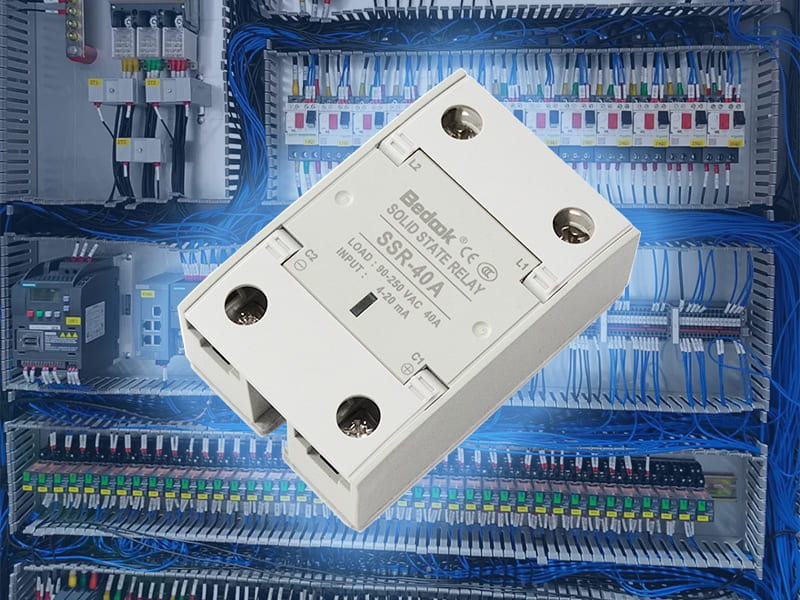

In the fast-changing field of electrical engineering, the Solid State Relay SSR is a cool and innovative part. Figuring out how to classify SSRs isn’t just some complicated tech talk. It’s super important if you want to use them to their fullest in all kinds of different projects. Do you wonder how these relays work, what different types there are, and which one would be just right for your project? Let’s start this exciting exploration together.
Solid State Relay SSR, a contactless switch in power electronics, is composed of microelectronic devices and power devices. The control end and the load end of SSR are electrically isolated. A tiny control signal at the input can be used to drive a high – current load.
Solid State Relay SSR Classification
Classification by the Number of AC Power Phases
Single-Phase SSR
Single-phase SSR is designed for single-phase AC circuits. It has only one pair of input and output terminals and can control an AC load of a single phase. It is often used for controlling single – phase – powered loads. By controlling the on-off of a single phase, it realizes the start-stop of the equipment. In the Classification of Solid State Relay SSR, single-phase SSRs play a crucial role in small-scale applications. For example, in household appliances and small office equipment, single-phase SSR can effectively control the power supply, ensuring the stable operation of these devices.
Three-Phase SSR
Three-phase SSR is applied in three-phase AC circuits. It has three sets of input and output terminals and can simultaneously control three-phase AC loads. Widely used in industrial fields for three-phase motors, large-scale heating equipment, and other three-phase-powered loads, it precisely coordinates the on-off of three-phase power supplies, ensuring the smooth operation of three-phase loads. In the context of the Classification of Solid State Relay SSR, three-phase SSR is indispensable for industrial applications. It can handle high-power loads and maintain the balance of three-phase power, which is crucial for the normal operation of industrial equipment.
Classification by Load Power Type
AC-Type Solid State Relay
AC-type solid-state relays are used to control AC loads. They can control conduction and cutoff in both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC power supply, adapting to the characteristics of the continuously changing direction of the AC voltage. They are widely used in the control of AC motors, AC lighting, and other devices that require AC power input. When considering the Classification of Solid State Relay SSR, AC-type SSR is a major category. Its ability to work with AC power makes it suitable for a wide range of applications where AC power is dominant, such as in factories, commercial buildings, and residential areas for powering various electrical appliances.
DC-Type Solid State Relay
DC-type solid state relays are specifically designed to control DC loads. Their output terminals can only be connected to a DC power supply. By controlling the on-off of DC, they control the operation of the load. They are commonly applied in devices such as DC motors and DC solenoids that rely on DC power supply. In the classification system of Solid State Relay SSR, DC-type SSR is an important part. It caters to the needs of DC-powered equipment, providing stable control for these devices in fields like robotics, automotive electronics, and some precision instruments.
Classification by Control Trigger Mode
Random – Conducting (Instantaneous – Switching) Solid State Relay
Immediate Activation on Signal Input
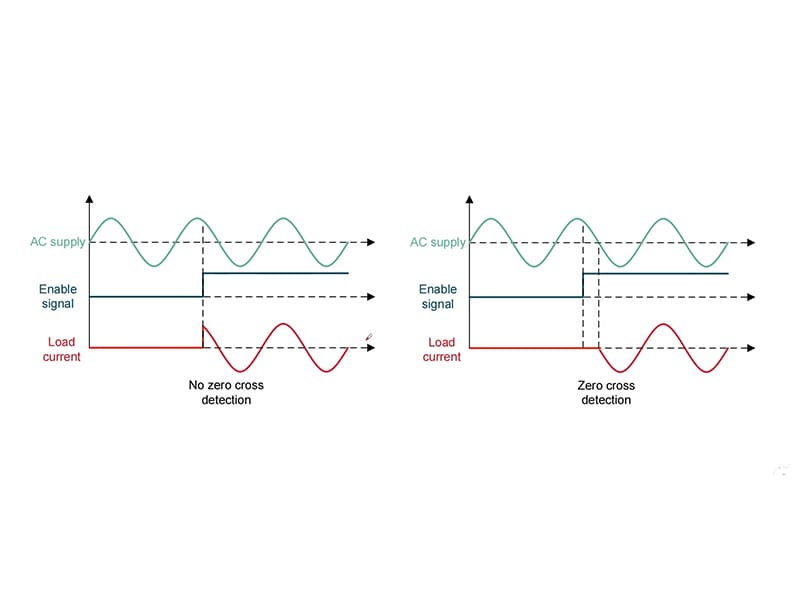
A random-conducting (instantaneous-switching) solid-state relay is a type of relay that can immediately turn on the load when a control signal is input, regardless of the phase of the AC power supply voltage.
Exceptionally Fast Response Speed
Its outstanding feature is its extremely fast response speed. It is capable of reacting to control signals within microseconds and quickly realizing the on – off control of the circuit. This characteristic makes it widely used in scenarios with strict requirements for switching speed. For instance, in some automated production equipment that requires rapid and precise control, high – frequency signal processing circuits, and certain electronic instruments that require instant response.
Drawbacks of Random-Conditioning Working Mode
However, the random-conduction (instantaneous-switching) working mode also brings some problems. Since it may turn on at any phase of the AC voltage, a large inrush current may be generated. This inrush current, in turn, causes harmonic interference, which affects the power grid and surrounding electronic devices.
Necessity of Anti – Anti-Interference Measures
Therefore, when using a random – conducting (instantaneous – switching) solid state relay, appropriate anti – interference measures often need to be taken according to specific situations. In the Classification of Solid State Relay SSR, random – conducting (instantaneous – switching) SSR has its unique application scenarios and challenges.
Zero-Cross-Triggering (Zero-Point Switching) Solid State Relay
Voltage-Dependent Activation and Deactivation
A zero – cross – triggering (zero – point switching) solid state relay is a relatively special relay. After a control signal is added, it will wait for the AC voltage to cross zero before turning on the output.
When the control signal is disconnected, it will also wait until the intersection point of the positive and negative half – cycles of the AC current, that is, the zero – potential point, before entering the off state.
Effective Harmonic and Pollution Avoidance
This working mode effectively avoids high – order harmonic interference and power grid pollution. Because when turning on and off at the zero – voltage crossing point, the current change is relatively stable, and no large inrush current is generated, thus reducing the generation of harmonics.
Applications in Sensitive Environments
Zero – cross – triggering (zero-point switching) solid-state relays are often used in scenarios with high requirements for electromagnetic compatibility. These include medical equipment, precision electronic instruments, communication equipment, and some industrial automation control systems with strict requirements for power grid quality. It can ensure that the equipment operates in a stable power supply environment, reducing the risk of equipment failure or performance degradation due to harmonic interference and providing reliable power control protection for various sensitive devices.
High Value in Anti – Anti-Anti-Anti-Interference Applications
In the Classification of Solid State Relay SSR, zero – cross – triggering (zero – point switching) SSR is highly valued for its anti – interference performance.
Performance Comparison between SSR and EMR
Advantages of SSR
- Long Lifespan: Since there are no mechanical moving parts, there are no problems such as contact wear and oxidation. Therefore, the service life of SSR is usually very long, reaching millions or even tens of millions of times, greatly reducing maintenance costs and replacement frequencies.
- Fast Switching Speed: It can complete on – off actions within microseconds, making it very suitable for scenarios with high requirements for response speed, such as high – frequency signal switching and rapid automation control.
- Low Noise and Arc – Free: During the working process, no mechanical noise is generated, and no arc appears when turning on and off. This not only reduces interference to the surrounding environment but also improves the safety of use, especially suitable for environments with high requirements for electromagnetic compatibility.
- Good Electrical Isolation: Good electrical isolation is achieved between the input and output through opto – couplers and other means, which can effectively prevent interference signals from the external circuit from entering the control circuit and also avoid the influence of the control circuit on the external circuit, improving the stability and reliability of the system.
Disadvantages of SSR
- Limited Overload Capacity: Compared with EMR, SSR has a poor overload capacity. Due to the sensitivity of its internal semiconductor devices to current and temperature, when the load current exceeds its rated value, the devices are likely to be damaged. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly control the load current during use.
- Conduction Voltage Drop: There is a certain voltage drop when conducting, which will generate a certain amount of heat on the solid state relay. Appropriate heat dissipation measures are required. If the heat dissipation is poor, it will affect its performance and lifespan and may even lead to equipment failure.
- High Cost: Due to the use of advanced semiconductor technology and manufacturing processes, the price of SSR is relatively high, which to a certain extent limits its application in some cost – sensitive fields.
Advantages of EMR
- Simple Structure and Low Cost: It is mainly composed of simple mechanical components such as iron cores, coils, armatures, and contacts. The structure is relatively simple, and the manufacturing process is mature, so the cost is low. It has a great advantage in some scenarios with high requirements for cost control.
- Strong Overload Capacity: It can withstand large inrush currents and can withstand load currents several times the rated current in a short time, suitable for some scenarios that require frequent starting and stopping of high – current loads, such as the control of large – scale motors.
- Good Voltage Withstand and Isolation Performance: The contacts can withstand high voltages when disconnected and have good electrical isolation performance, which can effectively isolate circuits with different potentials and ensure the safety and stability of the circuit.
Disadvantages of EMR
- Limited Lifespan: Due to the existence of mechanical moving parts, during frequent opening and closing actions, the contacts are prone to wear and oxidation, increasing contact resistance and even contact adhesion and other failures, thus limiting its service life. Regular maintenance and replacement are required.
- Slow Response Speed: The response speed is generally in milliseconds. Compared with the microsecond – level of SSR, the speed is slower. This makes it difficult to meet the needs in some scenarios with high requirements for fast response, such as high – speed data processing and high – frequency signal control.
- Arc and Noise Generation: Arcs are generated during the opening and closing of contacts, which not only interfere with surrounding electronic devices but also may cause safety hazards. At the same time, mechanical actions generate noise, which is restricted in some places with strict requirements for environmental noise.
Explore Bedook: Your Trusted Sensor Manufacturer
At Bedook, we specialize in designing, developing, and manufacturing a comprehensive range of proximity sensors and switches. Our extensive product lineup includes:
- Inductive Proximity Sensors
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors
- Photoelectric Sensors
- Ultrasonic Sensors
- Solid State Relays
- Various Accessories
With over 10,000 detailed product variations and a robust R&D team, we take pride in our ability to meet your unique requirements with tailored solutions and reliable performance.
Whether you’re seeking off-the-shelf products or customized designs, Bedook offers the expertise and production capacity to ensure your satisfaction.
Get in Touch Today!
We value your interest in our products and warmly encourage you to send us an inquiry. Let us help you find the perfect sensor solution for your application.
Thank you for considering Bedook—your trusted partner in innovation and quality manufacturing. We look forward to collaborating with you!