What is a Color Sensor: Principles, Comparisons and Diverse Applications

Step into a supermarket’s automated sorting area, and you’ll watch as plastic bottles of different colors glide into their proper bins. When you swap out printer ink cartridges, the machine always seems to know which one is red, yellow, or blue. On factory assembly lines, parts with off-color finishes get flagged and removed in a flash.
Behind all these seamless “color judgments” is an unsung hero: the color sensor. But what is a color sensor, exactly? How does it “see” colors, and what makes it different from other sensors? Today, let’s pull back the curtain on this clever technology.
What is a Color Sensor?
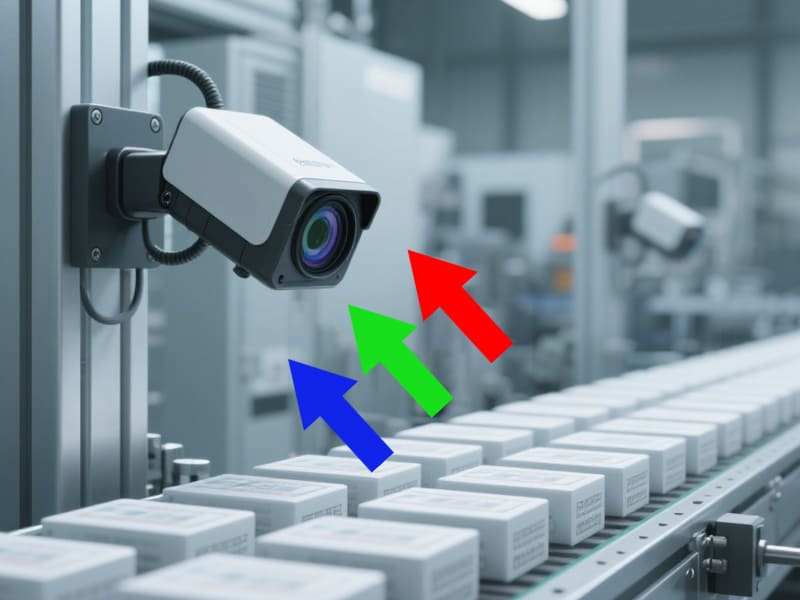
How Does a Color Sensor Work? Simulating the Human Eye’s “Optical Decoding”
Comparing Color Sensors with Other Proximity Sensors: Specialized “Detection Experts”
| Comparison Dimension | Color Sensor | Capacitive Sensor | Inductive Sensor | Ultrasonic Sensor | Ordinary Photoelectric Sensor |
| Core Detection Principle | Identifies colors/color differences (via RGB analysis) | Detects capacitance changes (using the object’s dielectric properties) | Detects inductance changes (via metal eddy currents) | Uses ultrasonic echo timing for distance/presence | Detects light blockage/reflection (for presence/distance) |
| Object Dependencies | Relies on color and reflectivity | Relies on the material’s ability to store electrical charge (good for non-metals) | Only reacts to metal objects | Works with any material (solids, liquids, gases) | Relies on how much light an object reflects/transmits |
| Best For | Color sorting, shade checks, and Appearance screening | Non-metal detection (plastics, liquids, fabrics) | Metal part tracking, counting | Long-range detection (tanks, obstacles, gaps) | Fast-moving object counting (conveyors, assembly lines) |
| Limitations | Struggles with glare or bright ambient light | Short range; sensitive to temperature/humidity | Only detects metal; easily 干扰 by nearby metals | Slow response; accuracy drops with temperature/wind | Confused by bright light; can’t tell colors apart |
| Everyday Examples | Fruit ripeness sorters, packaging color checks | Plastic bottle fill-level monitors, fabric edge detectors | Metal part counters, gear position sensors | Car backup sensors, grain silo level trackers | Elevator door sensors, vending machine item detectors |
So, if you need to sort red peppers from green ones, a color sensor is your pick. For checking how full a plastic bottle is, go with capacitive. And for counting steel bolts? Inductive is the way to go.
Diverse Applications of Color Sensors: From Factories to Homes
1. Industrial Manufacturing and Quality Checks
2. Food and Farming
3. Logistics and Packaging
4. Consumer Tech and Smart Homes
5. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Conclusion: Making Automation Smarter, One Color at a Time
Explore Bedook: Your Trusted Sensor Manufacturer
At Bedook, we specialize in designing, developing, and manufacturing a comprehensive range of proximity sensors and switches. Our extensive product lineup includes:
- Inductive Proximity Sensors
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors
- Photoelectric Sensors
- Ultrasonic Sensors
- Solid State Relays
- Various Accessories
With over 10,000 detailed product variations and a robust R&D team, we take pride in our ability to meet your unique requirements with tailored solutions and reliable performance.
Whether you’re seeking off-the-shelf products or customized designs, Bedook offers the expertise and production capacity to ensure your satisfaction.
Get in Touch Today!
We value your interest in our products and warmly encourage you to send us an inquiry. Let us help you find the perfect sensor solution for your application.
Thank you for considering Bedook—your trusted partner in innovation and quality manufacturing. We look forward to collaborating with you!