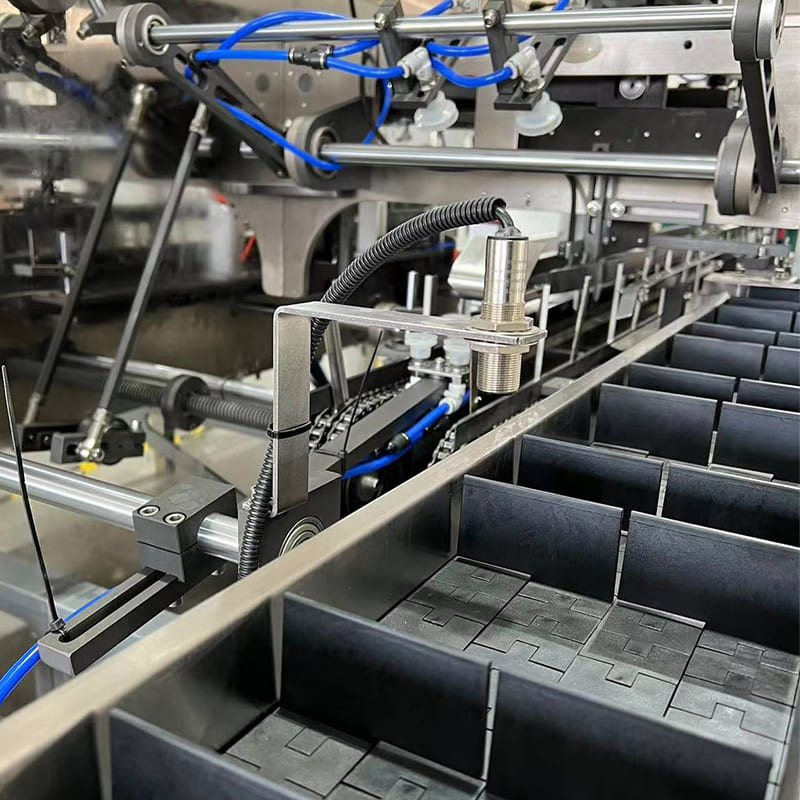
Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors VS High-Temperature Inductive Sensors

When selecting an inductive sensor for your industrial or commercial application, understanding the specific differences between Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors and High-Temperature Inductive Sensors is crucial. Although they share the same fundamental working principle, the environments they are designed for and their material composition differ significantly. This guide will help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
Similarities Between Wide Temperature and High-Temperature Inductive Sensors
Operating Principle:
Both sensor types operate based on the inductive sensing principle. This means they detect the presence of metal objects by generating an electromagnetic field and measuring changes in this field when a metal object enters it. This fundamental technology ensures reliable performance in various industrial applications.
Metal Detection Accuracy:
The precision in detecting metallic objects is consistent across both types of sensors. Whether you choose a wide temperature or high-temperature model, you can expect the same high level of repeatability and accuracy in metal detection.
Core Specifications:
In terms of key performance parameters like sensing distance and response time, both sensor types offer comparable performance. This ensures that the primary functional capabilities of these sensors remain reliable, regardless of the temperature conditions they are designed to withstand.
Key Differences Between Wide Temperature and High-Temperature Inductive Sensors
While the core functionalities are similar, the distinctions lie in their design, materials, and the environments they are intended for:
| Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors | High-Temperature Inductive Sensors | |
| Ingress Protection | IP67 | IP66 |
| Housing Material | Brass, nickel-plated | Stainless steel |
| Face Material | PBT | PEEK |
| Connectors | 2M PUR cable, 3*0.35mm² | 3M KFF46PH cable |
| Temperature Range | –40 °C to 85 °C | –25 °C to 230 °C |
| Key Characteristics | Low temperature resistance | High-precision stand-alone operation |
Ingress Protection:
Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors have a higher ingress protection rating (IP67) compared to High-Temperature Inductive Sensors (IP66). This makes wide temperature sensors more resistant to dust and water, offering better protection in harsh environments.
Material Composition:
Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors: Typically constructed with a brass, nickel-plated housing and a PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) face. These materials are chosen for their durability in cold and fluctuating temperature environments, providing stability and longevity.
High-Temperature Inductive Sensors: Feature a stainless steel housing with a PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) face. Stainless steel offers excellent resistance to high temperatures, while PEEK is known for its high thermal stability, making these sensors ideal for extreme heat conditions.
Operating Environment:
Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors: Designed to operate in environments with temperatures ranging from –40 °C to 85 °C. Their ability to withstand low temperatures makes them suitable for cold storage facilities, refrigeration systems, and outdoor applications in cold climates. The materials used in these sensors are specifically chosen for their low-temperature resistance, ensuring reliable operation in harsh, cold conditions.
High-Temperature Inductive Sensors: Built to endure temperatures from –25 °C to 230 °C. These sensors are ideal for high-temperature industrial environments such as automotive drying systems and the steel industry. Their high thermal resistance is achieved through the use of specialized materials that can maintain their structural integrity and performance even in extreme heat.
Characteristics and Applications of Each Sensor Type
Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors:
Features:
Wide operational temperature range from –40 °C to 85 °C.
High resistance to cold temperatures and fluctuations.
Robust construction with IP67 ingress protection, making them ideal for dusty and wet environments.
Applications:
Cold Storage Facilities: Monitor the presence of goods on shelves or the position of loading doors in environments where temperatures are consistently low.
Refrigeration Systems: Ensure the correct operation of moving parts, conveyor belts, or cooling systems in industrial refrigeration units.
Outdoor Applications in Cold Climates: Suitable for mining operations, oil and gas exploration, or asset tracking in freezing conditions.
Automotive Industry: Used in vehicles designed for cold climates, these sensors can detect the position of doors, windows, or seats, especially under cold start conditions.
Food Processing Plants: Reliable in areas where equipment needs to be cleaned with cold water or where ambient temperatures are low, ensuring the operation of machinery and product detection on production lines.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Critical in cleanrooms or other controlled environments with low temperatures, ensuring equipment control, monitoring, and maintaining the integrity of the production process.
Agricultural Machinery: Used in equipment that operates in cold climates or for refrigerated storage, ensuring proper operation and maintenance.
High-Temperature Inductive Sensors:
Features:
Designed to function in extremely high temperatures up to 230 °C.
Built with stainless steel and PEEK to withstand high heat while maintaining precision.
Typically have an IP66 rating, offering protection against dust and water but with a primary focus on thermal resistance.
Applications:
Automotive Industry: Essential in drying systems where body shells are heated to dry varnishes, these sensors monitor the position of skid carriers in environments with temperatures reaching up to 230 °C.
Steel Industry: Suitable for processes involving high temperatures, where reliable metal detection and sensor durability are critical.
Industrial Furnaces: Used to monitor the position of materials or components inside high-temperature furnaces, ensuring operational safety and efficiency.
Glass Manufacturing: Applicable in environments where high heat is used to shape and form glass, requiring precise detection and durability in extreme conditions.
Selecting the right inductive sensor for your application depends on the specific environmental conditions your system will face. Wide Temperature Inductive Sensors are your go-to choice for operations in cold or fluctuating temperatures, offering reliability and robustness in harsh environments. On the other hand, High-Temperature Inductive Sensors excel in extreme heat, providing precision and durability in high-temperature industrial settings.
Are you ready to optimize your system with the right sensor? Contact our sales team today to discuss your specific needs and find the perfect solution. Whether you require wide temperature resilience or high-temperature durability, our expert team is here to provide you with the best options tailored to your application.
Explore Bedook: Your Trusted Sensor Manufacturer
At Bedook, we specialize in designing, developing, and manufacturing a comprehensive range of proximity sensors and switches. Our extensive product lineup includes:
- Inductive Proximity Sensors
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors
- Photoelectric Sensors
- Ultrasonic Sensors
- Solid State Relays
- Various Accessories
With over 10,000 detailed product variations and a robust R&D team, we take pride in our ability to meet your unique requirements with tailored solutions and reliable performance.
Whether you’re seeking off-the-shelf products or customized designs, Bedook offers the expertise and production capacity to ensure your satisfaction.
Get in Touch Today!
We value your interest in our products and warmly encourage you to send us an inquiry. Let us help you find the perfect sensor solution for your application.
Thank you for considering Bedook—your trusted partner in innovation and quality manufacturing. We look forward to collaborating with you!